Dr Hilary Expresses His Dissaproval At Covid Restrictions Lifting Completely
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Experts from the UK Health Security Agency (UKHA) are closely monitoring hundreds of people over transmission fees. It comes after three cases were confirmed in England. NHS staff members who came into contact with the patients in Luton and Dunstable University Hospital and Addenbrooke’s hospital in Cambridge are also being monitored.
Many of these individuals will continue to be monitored for the rest of the month and into March, the Guardian reports.
According to the World Health Organisation (WHO),
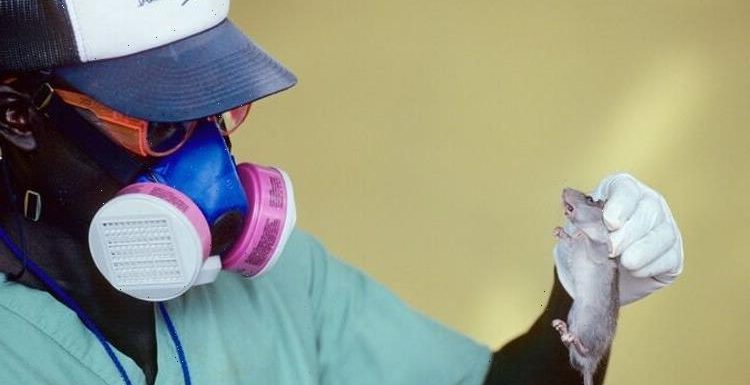
Lassa fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic illness caused by Lassa virus, a member of the arenavirus family of viruses.
Humans usually become infected with Lassa virus through exposure to food or household items contaminated with urine or faeces of infected Mastomys rats.


The disease is endemic in the rodent population in parts of West Africa.
Human-to-human transmissions are less likely, but can still occur – particularly in health care settings in the absence of adequate infection prevention and control measures.
Most people make a full recovery from the virus.
The overall case-fatality rate is 1 percent.
Among patients who are hospitalised with severe clinical presentation of Lassa fever, case-fatality is estimated at around 15 percent.

But experts say the return of Lassa fever to the UK after 13 years may be a sign of worst things to come.
Dr Melanie Saville, the director of vaccine development at the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), said: “The three confirmed cases of the potentially deadly Lassa fever in the UK, now very sadly including one death, are a stark reminder of our interconnected world and the need to continue to invest in outbreak preparedness and response efforts.
Emerging infectious diseases are increasing in prevalence, severity and spread as a result of climate change, global transportation and human encroachment into previously isolated areas,”
Dr Saville offed that there is an “urgent need for vaccines”.
CEPI is now advancing the development of six Lassa fever vaccines.
DON’T MISS:
Call for tougher rules as new variant may be ‘more lethal’ [SPOTLIGHT]
Putin to hit back and cut THREE key exports to West [HIGHLIGHT]
China faces crisis after ‘alarming’ children’s heart discovery [REVEAL]


Now, the largest-ever Lassa fever study, called Enable, has been launched to provide a more accurate assessment of the virus.
More than 20,000 people are being recruited to take part in the study, which will provide key information to help develop a jab.
Dr Saville is not alone in her warning and joins many other scientists who fear lessons have not been learned from Covid-19 about the need to properly fund pandemic preparedness.
Professor Dame Sarah Gilbert, the brains behind the AstraZeneca vaccine said in October: “We’ve actually gone backwards in terms of the work we’re doing on development of vaccines for the outbreak pathogens before the pandemic.
“It’s just really slowed right down.
“Trying to get that moving again is really difficult and the funding still isn’t there to move that on.”
Source: Read Full Article